Although Tristan Did Well in Statistics in High School as an Art Major in College Quizlet

A post-secondary graduate receives a diploma during a graduation ceremony.
Higher pedagogy is tertiary education leading to honor of an bookish degree. College didactics, besides called post-secondary instruction, third-level or 3rd education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completion of secondary instruction. It represents levels 6, 7 and 8 of the 2011 version of the International Standard Classification of Education structure. 3rd education at a non-degree level is sometimes referred to as further education or standing education as distinct from higher education.
The right of admission to higher education [edit]
The correct of access to higher education is mentioned in a number of international human rights instruments. The UN International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights of 1966 declares, in Commodity thirteen, that "higher teaching shall exist made equally attainable to all, on the basis of capacity, by every advisable means, and in particular by the progressive introduction of free education". In Europe, Article 2 of the Get-go Protocol to the European Convention on Human being Rights, adopted in 1950, obliges all signatory parties to guarantee the right to pedagogy.
Definition [edit]
Higher education, also chosen post-secondary teaching, third-level or 3rd educational activity, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after completion of secondary instruction.[ citation needed ].This consists of Universities, Colleges and Polytechnics that offering formal degrees beyond high school or secondary school didactics.
The International Standard Classification of Teaching in 1997 initially classified all tertiary didactics together in 1997 version of its schema. They were referred to every bit level 5 and doctoral studies at level 6. In 2011, this was refined and expanded 2011 version of the structure. Higher education at undergraduate level, masters and doctoral level became levels 6, 7 and 8. Non-caste level Tertiary pedagogy, sometimes referred to equally further teaching or standing didactics was reordered ISCED 2011 level 4, with level 5 for some higher courses.[1]
In the days when few pupils progressed across primary education or basic instruction, the term "higher education" was often used to refer to secondary education, which can create some defoliation.[note one] This is the origin of the term high schoolhouse for various schools for children betwixt the ages of 14 and 18 (United States) or 11 and 18 (UK and Australia).[ii]
Providers [edit]

In the US, college pedagogy is provided by universities, academies, colleges, seminaries, conservatories, and institutes of applied science, and certain college-level institutions, including vocational schools, universities of practical sciences, trade schools, and other career-based colleges that award degrees. Tertiary educational activity at non-caste level is sometimes referred to as further education or standing educational activity as distinct from higher teaching.[3] [iv]
Higher education includes teaching, research, exacting practical work (e.g. in medical schools and dental schools), and social services activities of universities.[5]
Inside the realm of teaching, it includes both the undergraduate level, and beyond that, graduate-level (or postgraduate level). The latter level of teaching is ofttimes referred to as graduate schoolhouse, especially in N America. In add-on to the skills that are specific to any item degree, potential employers in any profession are looking for show of disquisitional thinking and analytical reasoning skills, teamworking skills, data literacy, ethical judgment, decision-making skills, fluency in speaking and writing, problem solving skills, and a wide knowledge of liberal arts and sciences.[vi]
History [edit]
| |||
| House of Life "library" | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Egyptian hieroglyphs |
The oldest known institutions of higher teaching are credited to Dynastic Egypt, with Pr-Anx (houses of life) built every bit libraries and scriptorium, containing works on law, compages, mathematics, and medicine, and involved in the training of "swnw" and "swnwt" (male and female Doctors); extant Egyptian papyri from the 3rd millennia BC, are in several collections.[7]
In the Greek world, Plato's Academy (c. 387 - 86 BC), Aristotle's Lycaeum (c. 334 - 86 BC) and other philosophical-mathematical schools became models for other establishments, particularly in Alexandria of Egypt, under the Ptolemies.
In South Aisia, the city of Takṣaśilā[ when? ], later the great Buddhist monastery of Nālandā (c. 427 - 1197 CE), attracted students and professors fifty-fifty from distant regions.[8]
In Red china, the Han dynasty established chairs to teach the Five Confucean Classics, in the Grand Schoolhouse, Taixue (c. 3 - 1905 CE), to train cadres for the imperial administration.[ix] [10] All these higher-learning institutions became models for other schools within their sphere of cultural influence.[ commendation needed ]
In 425 CE, the Byzantine emperor Theodosius Two innovated as he established the Pandidakterion, with a faculty of 31 professors, to railroad train public servants. In the 7th and 8th centuries, "cathedral schools" were created in Western Europe. Meanwhile, the first Medresahs were founded in the Moslem empire – initially mere primary schools in the premises of major mosques, which gradually evolved toward secondary, afterward college education. Even so loftier the intellectual level of these schools could be, information technology would exist anachronistic to call them "universities". Their organisation and purposes were markedly different from the corporations of students and teachers, contained from both the Church and the State, which established themselves from the 12th century in Western Europe every bit Universitas Studiorum.[ citation needed ]
According to UNESCO and Guinness World Records, the University of al-Qarawiyyin in Fez, Morocco is the oldest existing continually operating college educational institution in the world.[11] [12] and is occasionally referred to as the oldest academy past scholars.[xiii] Undoubtedly, in that location are older institutions of college education, for example, the University of Ez-Zitouna in Montfleury, Tunis, was first established in 737. The oldest university in the globe is the University of Bologna, founded in 1088.[14] [xv] [xvi] [17] [18]
20th century [edit]
Since Earth State of war II, developed and many developing countries accept increased the participation of the age grouping who mostly studies college teaching from the elite charge per unit, of up to 15 per cent, to the mass rate of 16 to fifty per cent.[19] [20] [21] In many developed countries, participation in college education has connected to increment towards universal or, what Trow afterward called, open access, where over one-half of the relevant age group participate in higher education.[22] Higher educational activity is important to national economies, both as an industry, in its ain right, and as a source of trained and educated personnel for the residue of the economy. College educated workers have commanded a measurable wage premium and are much less probable to become unemployed than less educated workers.[23] [24]
21st century [edit]
In recent years, universities accept been criticized for permitting or actively encouraging grade inflation.[25] [26] As well, the supply of graduates in many fields of study is exceeding the demand for their skills, aggravating graduate unemployment, underemployment, overqualification, credentialism and educational inflation.[27] [28] Some commentators have suggested that the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on education is speedily making sure aspects of the traditional college pedagogy organization obsolete.[29]
Types of provider in the United states of america [edit]
The general higher education and preparation that takes place in a university, college, or Plant of technology usually includes significant theoretical and abstract elements, likewise as applied aspects (although limited offerings of internships or SURF programs endeavour to provide practical applications). In contrast, the vocational higher education and training that takes identify at vocational universities and schools usually concentrates on practical applications, with very petty theory.
In addition, professional-level instruction is always included within Higher Education, and unremarkably in graduate schools since many postgraduate academic disciplines are both vocationally, professionally, and theoretically/inquiry oriented, such every bit in the constabulary, medicine, pharmacy, dentistry, and veterinary medicine. A basic requirement for entry into these graduate-level programs is almost always a bachelor's degree, although alternative ways of obtaining entry into such programs may be available at some universities. Requirements for admission to such high-level graduate programs is extremely competitive, and admitted students are expected to perform well.
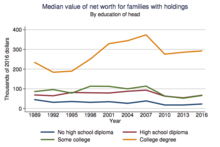
Mean financial wealth of The states families past didactics of the head of household, 1989-2010

Mean income of U.s. families by education of the head of household, 1989-2010
When employers in any profession consider hiring a college graduate, they are looking for prove of disquisitional thinking, analytical reasoning skills, teamworking skills, information literacy, upstanding judgment, conclusion-making skills, communication skills (using both text and speech), problem solving skills, and a wide cognition of liberal arts and sciences. Nevertheless, most employers consider the average graduate to exist more or less scarce in all of these areas.[30] [31] [32]
In the United states of america, there are large differences in wages and employment associated with unlike degrees. Medical doctors and lawyers are generally the highest paid workers, and accept among the everyman unemployment rates. Among undergraduate fields of study, scientific discipline, engineering science, engineering, math, and business generally offering the highest wages and best chances of employment, while teaching, communication, and liberal arts degrees generally offer lower wages and a lower likelihood of employment.[23] [33]
Liberal arts [edit]
Bookish areas that are included inside the liberal arts include great books, history, languages including English language, linguistics, literature, mathematics, music, philosophy, political science, psychology, religious studies, scientific discipline, ecology scientific discipline, sociology and theater.
Engineering science [edit]
Pedagogy engineering is pedagogy the application of scientific, economical, social, and applied noesis in social club to design, build, maintain, and improve structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes. It may encompass using insights to conceive, model and scale an advisable solution to a problem or objective. The subject field of engineering is extremely broad, and encompasses a range of more than specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis on detail areas of engineering and types of awarding. Engineering disciplines include aerospace, biological, civil, chemical, calculator, electric, industrial and mechanical.
Performing arts [edit]
The performing arts differ from the plastic arts or visual arts, insofar every bit the one-time uses the artist'south own body, confront and presence as a medium; the latter uses materials such as clay, metal or pigment, which can be molded or transformed to create a piece of work of art.
Performing arts institutions include circus schools, trip the light fantastic toe schools, drama schools and music schools.
Plastic or visual arts [edit]
The plastic arts or visual arts are a class of art forms, that involve the employ of materials, that can be moulded or modulated in some way, often in three dimensions. Examples are painting, sculpture, and drawing.
Higher educational institutions in these arts include flick schools and art schools.
Vocational [edit]
College vocational education and training takes place at the non-university tertiary level. Such teaching combines teaching of both practical skills and theoretical expertise. Higher teaching differs from other forms of mail-secondary educational activity such every bit that offered by institutions of vocational education, which are more colloquially known as trade schools. Higher vocational education might be contrasted with instruction in a usually broader scientific field, which might concentrate on theory and abstract conceptual knowledge.
Professional higher education [edit]
This describes a distinct form of higher education that offers a particularly intense integration with the world of piece of work in all its aspects (including didactics, learning, inquiry and governance) and at all levels of the overarching Qualifications Framework of the European Higher Teaching Surface area. Its function is to diversify learning opportunities, enhance employability, offer qualifications and stimulate innovation, for the do good of learners and guild.
The intensity of integration with the globe of work (which includes enterprise, civil society and the public sector) is manifested by a strong focus on application of learning. This approach involves combining phases of piece of work and study, a business concern for employability, cooperation with employers, the utilize of do-relevant noesis and use-inspired research.[34]
Examples of providers of professional higher education may include graduate colleges of architecture, business concern, journalism, law, library science, optometry, pharmacy, public policy, homo medicine, professional engineering, podiatric medicine, scientific dentistry, K-12 educational activity, and veterinarian medicine.
Statistics [edit]
A 2014 report past the Organisation for Economical Co-operation and Development states that by 2014, 84 percent of young people were completing upper secondary educational activity over their lifetimes, in high-income countries. Tertiary-educated individuals were earning twice as much as median workers. In contrast to historical trends in education, young women were more likely to consummate upper secondary education than young men. Additionally, access to teaching was expanding and growth in the number of people receiving university education was ascent sharply. By 2014, close to forty percent of people anile 25–34 (and around 25 percent of those aged 55–64), were existence educated at university.[35]
Recognition of studies [edit]
The Lisbon Recognition Convention stipulates that degrees and periods of study must be recognised in all of the Signatory Parties of the convention.[36]
Run into also [edit]
- Category:Higher didactics past land
- List of higher education associations and alliances
- College and academy rankings
- Governance in higher education
- Graduation
- Higher education accreditation
- Higher education bubble
- Higher teaching policy
- Higher Teaching Price Index
- Institute
- UnCollege
- Hochschule
- League of European Research Universities
- Technical and Further Educational activity (TAFE)
Notes [edit]
- ^ For example, Higher Education: General and Technical, a 1933 National Union of Teachers pamphlet by Lord Eustace Percy, which is really nearly secondary education and uses the two terms interchangeably.
References [edit]
- ^ Revision of the International Standard Nomenclature of Education (ISCED), retrieved 05-04-2012.
- ^ "high school". lexicon.cambridge.org.
- ^ "The Difference Betwixt Continuing Educational activity and Professional Development". www.columbiasouthern.edu . Retrieved 2021-x-17 .
- ^ "6 Reasons Why Continuing Education Is Important". Western Governors University . Retrieved 2021-10-17 .
- ^ Pucciarelli F., Kaplan Andreas M. (2016) Competition and Strategy in College Education: Managing Complication and Uncertainty, Business Horizons, Volume 59
- ^ "Employers Judge Recent Graduates Ill-Prepared for Today'southward Workplace, Endorse Wide and Project-Based Learning as All-time Training for Career Opportunity and Long-Term Success" (Press release). Washington, DC: Association of American Colleges and Universities. 20 January 2015. Archived from the original on 12 Apr 2017. Retrieved xi April 2017.
- ^ Gordan, Andrew H.; Shwabe, Calvin W. (2004). The Quick and the Dead: Biomedical Theory in Ancient Egypt. Egyptological Memoirs. Leiden: Brill Academic Publishers. p. 154. ISBN978-xc-04-12391-v.
- ^ Radha Kumud Mookerji, Aboriginal Indian instruction: Brahmanical and Buddhist (2nd ed.). Delhi, Motilal Banarsidass, 1989
- ^ Étienne Balazs, La Bureaucratie céleste (recherches sur l'économie et la société de la Chine traditionnelle), Paris, Gallimard, 1968
- ^ Peter Tze Ming Ng, « Paradigm Shift and the State of the Field in the Study of Christian Higher Instruction in China », in Cahiers d'Extrême-Asie, 2001, n° 12, pp. 127-140
- ^ "Oldest college-learning institution, oldest university". Guinness Globe Records.
- ^ "Medina of Fez". UNESCO Earth Heritage Centre. UNESCO. Retrieved seven Apr 2016.
- ^ Verger, Jacques: "Patterns", in: Ridder-Symoens, Hilde de (ed.): A History of the University in Europe. Vol. I: Universities in the Middle Ages, Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN 978-0-521-54113-8, pp. 35–76 (35)
- ^ Superlative Universities Archived 17 January 2009 at the Wayback Motorcar Earth University Rankings Retrieved half-dozen Jan 2010
- ^ Paul L. Gaston (2010). The Challenge of Bologna. p. 18. ISBN978-i-57922-366-iii . Retrieved vii July 2016.
- ^ Hunt Janin: "The university in medieval life, 1179–1499", McFarland, 2008, ISBN 0-7864-3462-7, p. 55f.
- ^ de Ridder-Symoens, Hilde: A History of the Academy in Europe: Volume ane, Universities in the Center Ages, Cambridge University Press, 1992, ISBN 0-521-36105-two, pp. 47–55
- ^ mondial, UNESCO Centre du patrimoine. "The Porticoes of Bologna - UNESCO Globe Heritage Centre". UNESCO Heart du patrimoine mondial (in French). Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- ^ Trow, Martin (1973) Problems in the transition from elite to mass higher education. Carnegie Commission on College Education, Berkeley, http://world wide web.eric.ed.gov/ERICWebPortal/search/detailmini.jsp?_nfpb=true&_&ERICExtSearch_SearchValue_0=ED091983&ERICExtSearch_SearchType_0=no&accno=ED091983, accessed 1 August 2013
- ^ Brennan, John (2004) The social office of the gimmicky university: contradictions, boundaries and modify, in Center for Higher Education Research and Information (ed.)
- ^ Ten years on: changing educational activity in a changing world (Buckingham: The Open Academy Printing), https://www.open up.ac.uk/cheri/documents/ten-years-on.pdf Archived 2017-05-25 at the Wayback Machine, accessed 9 Feb 2014
- ^ Trow, Martin (2007) [2005] Reflections on the transition from aristocracy to mass to universal admission: forms and phases of higher education in mod societies since WWII, Springer International Handbooks of Education book 18, 2007, 243-280
- ^ a b Simkovic, Michael (2011-09-05). "Risk-Based Pupil Loans". SSRN 1941070.
- ^ OECD, Education at a Glance (2011)
- ^ Gunn, Andrew; Kapade, Priya (25 May 2018), "The academy grade aggrandizement debate is going global", Academy Earth News , retrieved 23 June 2019,
The grading process has been compromised equally universities are incentivised to meet the demands of their customers and graduate more than students with top grades to boost their institutional ranking.
- ^ Baker, Simon (June 28, 2018), "Is grade inflation a worldwide trend?", The Earth University Rankings, Times Higher Educational activity, retrieved June 23, 2019,
Departments where enrollments were falling felt under pressure to relax their grading practices to brand their courses more attractive, leading to an "arms race" in course aggrandizement.
- ^ Coates, Ken; Morrison, Pecker (2016), Dream Factories: Why Universities Won't Solve the Youth Jobs Crunch, Toronto: Dundurn Books, p. 232, ISBN9781459733770
- ^ Brown, Phillip; Lauder, Hugh; Ashton, David (2012), The Global Auction: The Cleaved Promises of Education, Jobs, and Incomes, Oxford University Press, p. 208, ISBN9780199926442
- ^ Kaplan, Andreas (2021), Higher teaching at the crossroads of disruption: the academy of the 21st century, Emerald Publishing, ISBN9781800715042
- ^ "Employers Estimate Recent Graduates Ill-Prepared for Today's Workplace, Endorse Broad and Project-Based Learning as All-time Preparation for Career Opportunity and Long-Term Success" (Press release). Washington, DC: Association of American Colleges and Universities. 20 Jan 2015. Archived from the original on 12 April 2017. Retrieved 11 Apr 2017.
- ^ Crowley, Elizabeth (25 October 2019). "Tackling the future 'man' skills deficit together". Chartered Constitute of Personnel and Development . Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ "Employers Say Students Aren't Learning Soft Skills in College". Social club for Man Resource Management. October 21, 2019. Retrieved Dec 4, 2020.
- ^ "The Economical Value of College Majors" (Printing release). Georgetown University. May 2015. Retrieved 17 Baronial 2016.
- ^ "Harmonising Approaches to Professional College Didactics in Europe". Harmonising Approaches to Professional College Pedagogy in Europe. EURASHE. 2013. Archived from the original on July 4, 2013. Retrieved 2014-10-17 .
- ^ Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (September 2014). "Higher levels of instruction paying off for young, says OECD". Archived from the original on June 28, 2013. Retrieved September 11, 2014.
- ^ "Lisbon Recognition Convention". coe.int . Retrieved 28 May 2019.
Further reading [edit]
- Alkamel, Mohammed Adulkareem A.; Chouthaiwale, Santosh S.; Yassin, Amr Abdullatif; AlAjmi, Qasim; Albaadany, Hanan Yahia (March 2021). "Online Testing in Higher Pedagogy Institutions During the Outbreak of COVID-19: Challenges and Opportunities". In Arpaci, Ibrahim; Al-Emran, Mostafa; Al-Sharafi, Mohammed A.; Marques, Gonçalo (eds.). Emerging Technologies During the Era of COVID-nineteen Pandemic. Studies in Systems, Determination and Control. Vol. 348. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Nature. pp. 349–363. doi:ten.1007/978-iii-030-67716-9_22. ISBN978-3-030-67715-2. PMC7980164. S2CID 232322223.
- Kaplan, Andreas (2021). College Instruction at the Crossroads of Disruption: The University of the 21st Century. Emerald. ISBN978-ane-80071-504-2.
External links [edit]
- Association for the Report of Higher Education
- American Educational Research Association
- World Bank Tertiary Didactics
maitlandwitena1952.blogspot.com
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Higher_education